Refugees have fled from war, persecution, poverty, famine and pestilence over the ages. However, there is no documented record of refugees fleeing climate change, though a single resident of Tuvalu attempted to have himself accepted as a climate change refugee without success. MIT recently published an article reporting on the World Bank Groundswell Report which suggests that up to 216 million people might be required to migrate within their own countries as “climate shocks” occur.
“Climate change is a powerful driver of internal migration because of its impacts on people’s livelihoods and loss of livability in highly exposed locations. By 2050, Sub-Saharan Africa could see as many as 86 million internal climate migrants; East Asia and the Pacific, 49 million; South Asia, 40 million; North Africa, 19 million; Latin America, 17 million; and Eastern Europe and Central Asia, 5 million.”
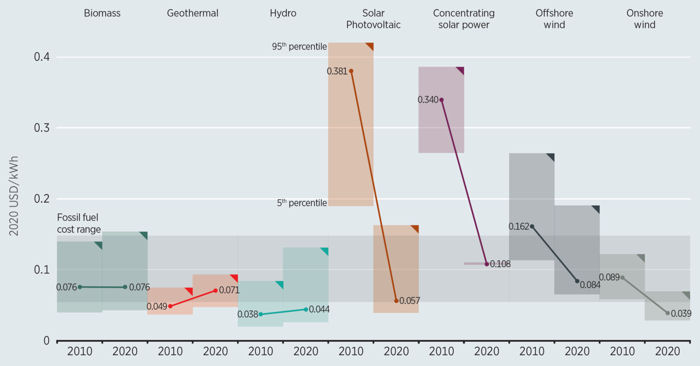
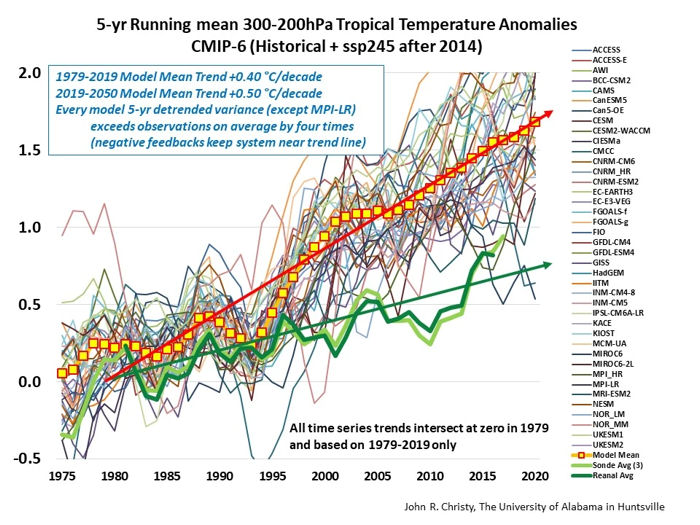
These projections are all based on the unvalidated and unverified climate models in the CMIP5 ensemble of models and would be expected to be even worse using the CMIP6 ensemble of models, which project even more rapid and extreme temperature increases. Such studies typically employ the extreme Resource Concentration Pathway (RCP 8.5), which has frequently been described as the “business as usual” scenario, though it has more recently been identified as extremely unlikely by numerous researchers.
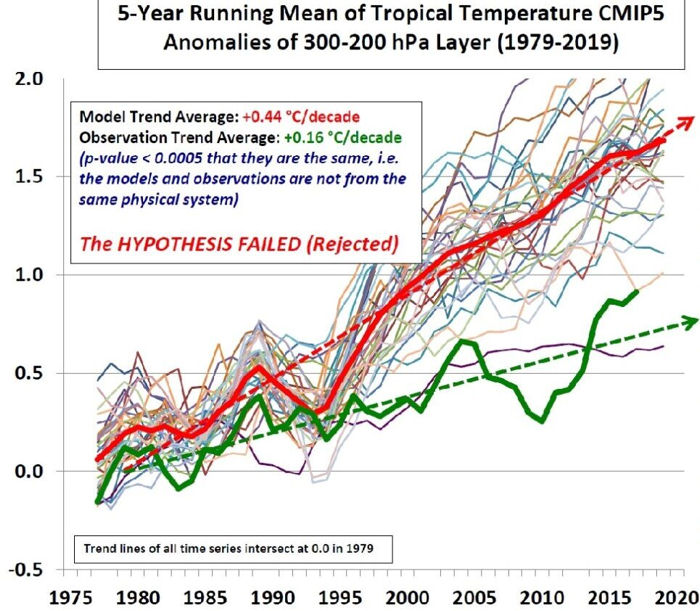
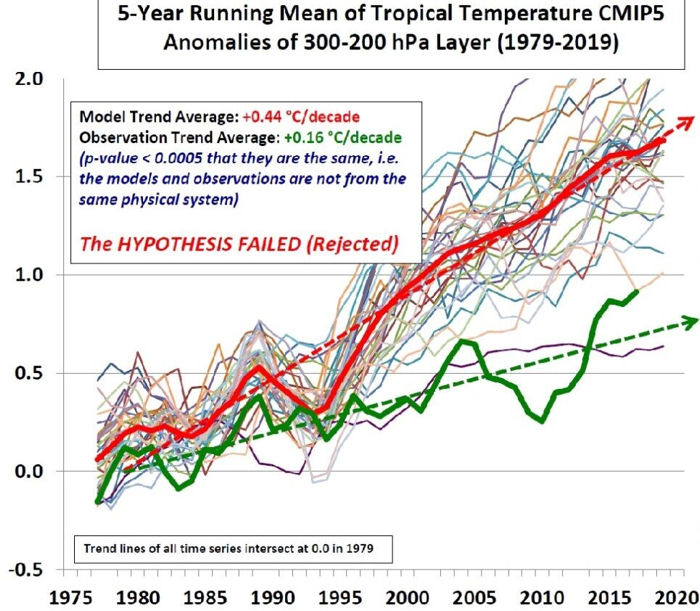
There is growing recognition that the climate models are “running hot”, projecting greater temperature anomaly increases than are observed in the real climate. The graph below, prepared by Dr. John Christy compares the model outputs with observations. Christy concludes that the hypothesis upon which the models were based has “failed”. This failure is the result of the use of high climate sensitivity to CO2, RCP 8.5 and the assumption of positive cloud feedback.
The historical observations strongly suggest that the likelihood of future “climate shocks”, particularly in the near term, is far lower than the models would project. This is consistent with recent research estimating lower climate sensitivity to CO2 and with satellite observations which suggest the cloud feedback is negative.
Note that, in the quote reproduced above from the World Band Groundswell Report, the authors state that “climate change IS a powerful driver of internal migration”, not that it might become such a driver. Yet climate change is not currently driving internal or external migration.
The primary issues of concern regarding migration are temperature increases and sea level rise. The report appears to ignore the fact that, in most regions, observed temperature increases are primarily warmer nighttime temperatures, not higher daytime temperatures. The report also appears to ignore the positive impacts of increased CO2 concentrations on global greening and the efficiency with which plants use available water.
The report also appears to ignore the fact that sea level has been rising at a consistent rate since the trough of the Little Ice Age. The rise of sea level from the Little Ice Age to the modern warm period is certainly climate change, but it is not likely attributable to increased atmospheric CO2 concentrations.
 The Right Insight is looking for writers who are qualified in our content areas. Learn More...
The Right Insight is looking for writers who are qualified in our content areas. Learn More...